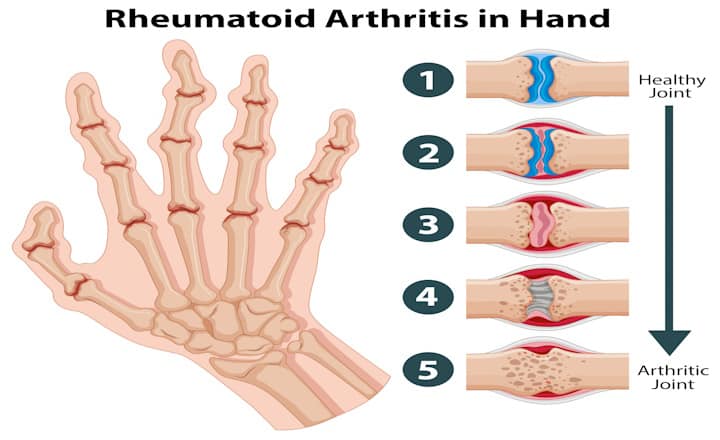
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disorder that primarily affects the joints but can also impact other systems of the body. Unlike the wear-and-tear damage of osteoarthritis, RA affects the lining of the joints, causing a painful swelling that can eventually lead to joint deformity and erosion of bone. This progressive and debilitating disease often leads to severe pain, fatigue, and impaired physical function. Significantly impacting the quality of life of those affected.
Symptoms
Joint pain, stiffness, and swelling are the prevalent symptoms associated with rheumatoid arthritis. These symptoms typically affect multiple joints simultaneously and have a symmetrical pattern, meaning that they occur on both sides of the body equally. The joints of the hands, wrists, feet, ankles, and knees are commonly affected in RA. Other possible symptoms may include:
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
- Inflammation can affect various organs, including the eyes, lungs, and heart.
- Experiencing numbness or tingling sensations in the hands and feet can be indicative of certain medical conditions.
Signs of Rheumatoid arthritis
The diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis is based on a combination of laboratory tests, imaging scans, and physical examination findings. Some common signs of RA include:
- Joint stiffness and tenderness
- Swelling or warmth in the affected joints
- Experiencing prolonged morning stiffness lasting beyond 30 minutes.
- Presence of rheumatoid nodules (small bumps under the skin, commonly found on the elbows)
- Positive rheumatoid factor or anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies in blood tests
Causes
The exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis is not fully understood. However, it is believed to result from a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Some risk factors that have been identified include:
- Family history of RA
- Age (typically develops between the ages of 30 and 60)
- Gender (more common in women than men)
- Smoking
- Obesity
Treatment
There is currently no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, but there are various treatment strategies available to help manage symptoms, slow the progression of the disease, and improve quality of life. These may include:
- Medications, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), are commonly used to treat various conditions.
- Physical therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Regular exercise
- Rest and joint protection techniques
- Heat or cold therapy
In some cases, surgery may also be recommended to repair or replace damaged joints. It is important to work closely with a healthcare team to develop an individualized treatment plan and monitor the disease’s progression. Additionally, making lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing stress can also help improve symptoms and overall well-being for individuals living with rheumatoid arthritis.
Cope with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Living with rheumatoid arthritis can be challenging, both physically and mentally. It is essential to take care of your overall health and well-being to better cope with the disease’s impact. Some tips for managing RA include:
- Seek support from family, friends, or a support group
- Keep a positive attitude
- Educate yourself about the disease and treatment options
- Take care of your mental health by practicing relaxation techniques or seeking therapy
- Follow a healthy, balanced diet
- Listen to your body and pace yourself
Does rheumatoid arthritis worsen as one age?
There is no definitive answer to whether rheumatoid arthritis gets worse with age. Some individuals may experience less severe symptoms as they get older, while others may have a more progressive form of the disease. However, it is essential to continue managing symptoms and seeking proper treatment regardless of age to maintain functionality and quality of life. As the disease progresses, adjustments in treatment plans may be necessary, and regular monitoring is crucial to detect any potential complications. As always, it is vital to work closely with a healthcare team to address any concerns or changes in symptoms.
Is it possible to achieve recovery from rheumatoid arthritis?
While there is currently no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, it is possible to achieve remission with early and aggressive treatment. However, symptoms can return, and the disease can continue to progress, requiring ongoing management. It is also essential to note that individuals may respond differently to treatments, and achieving remission may not be possible for everyone. The focus should be on managing symptoms and improving overall well-being to lead a fulfilling life with this chronic disorder.
Conclusion
Rheumatoid arthritis is a complex and chronic disease that requires ongoing management and care. It is crucial to seek proper treatment, make lifestyle adjustments, and take care of mental health to better cope with the impact of RA. While there is no cure for this disease. It is possible to achieve remission and improve quality of life with the right support and self-care practices. Remember to listen to your body, seek help when needed, and stay informed about new treatment options. With proper care and management, individuals living with rheumatoid arthritis can continue to lead fulfilling lives.

